

Miles Lancaster
September 20th, 2023
As the world continues to rapidly digitize, many organizations face new operational challenges. These challenges have real-world consequences. Consider the 2023 FFA systems failure: an internal systems error that resulted in thousands of flight delays globally, which led to millions of dollars lost for both airlines and their countries.
Operational defects are at the heart of a surprising number of these disruptions, often causing delays or complete system shutdowns which lead to significant costs. These software defects are often overlooked as teams focus on security vulnerabilities. But not dealing with these bugs can be costly. Based on Gartner data, the annual cost of vendor operational defects to an average enterprise company is at least $6.5 million!
Not only are individual organizations taking preventive measures, but nations are also enacting regulations. For example, the EU’s newly proposed Digital Operations Resilience Act (DORA) aims to safeguard financial institutions from internal operational defects.
Important to observe for IT and GRC leaders is that this regulation goes beyond cybersecurity, requiring “operational resilience” in all areas of IT Risk, including third-party providers. For organizations to be compliant by January 2025, they need specialized tools that detect vendor software bugs. These defects are one of the biggest threats to resiliency. Yet many organizations are exposed in this area because they mistakenly believe that their security solutions are addressing this risk.
Below, we dive into this new regulation for EU financial entities and what must be done to comply.
While many financial institutions are cognizant of security vulnerabilities, they must also be informed about the risk of operational defects. The difference is that security vulnerabilities are weaknesses in systems that could be triggered by a threat, while operational defects are software bugs that affect the integrity or availability of IT systems.
“All sources of ICT risks should be continuously identified in order to set-up protection and prevention measures.” - PWC
The DORA EU legislation provides directives to protect financial institutions from both security vulnerabilities and operational defects. Some of the main directives of the legislation include:
“‘Digital Operational Resilience’ means the ability of a financial entity to build, assure and review its operational integrity and reliability by ensuring, either directly or indirectly through the use of services provided by ICT third-party service providers, the full range of ICT-related capabilities needed to address the security of the network and information systems which a financial entity uses, and which support the continued provision of financial services and their quality.” - DORA Chapter 1, Article 3
What it means: Digital Operational Resilience means the resilience of financial institution’s IT capabilities, and associated third-party capabilities, required to ensure their financial services are impervious to disruption.
This regulation specifically pertains to financial institutions. The entities that the EU considers in scope is fairly broad – including “credit institutions, payment institutions, e-money institutions, investment firms, crypto asset service providers, central securities depositories, managers of alternative investment funds, UCITS management companies, administrators of critical benchmarks, crowdfunding service providers, and ICT third-party service providers.”
In other words, many companies that were not previously subject to these types of regulations are within the scope of DORA!
“‘ICT Risk’ means any reasonably identifiable circumstance in relation to the use of network and information systems which, if materialised, may compromise the security of the network and information systems, of any technology dependent tool or process, of operations and processes, or of the provision of services by producing adverse effects in the digital or physical environment;” - DORA Chapter 1, Article 3
What it means: Anything that may interfere with the stability or security of internal and third-party IT capabilities, upon which financial services are dependent.
“Put in place policies that aim to ensure the maintenance of high standards of availability, authenticity, integrity and confidentiality, of data;” - DORA Chapter 2, Article 5
What it means: DORA not only requires managing confidentiality risks in the form of cybersecurity, but also risks to the availability, authenticity, and integrity of both internal and third-party IT capabilities.
Operational resilience against IT vendor defects is a central focus of the DORA legislation. DORA provides clear rules on digital safety, dictating how financial firms must handle IT risks, report incidents, and test their IT systems. Recognizing the reliance firms have placed on third-party software, the EU DORA regulation aims to reduce risks stemming from this dependence.
“DORA brings an operational resilience view to the EU FS regulatory framework for the first time, replacing the previous patchwork of cyber and IT risk-focused guidelines with a new holistic approach to building resilience against digital disruptions.” - Deloitte
With the enforcement date of January 2025, financial institutions operating in the EU must take the necessary measures to ensure their firm is compliant. Financial firms who operate in the EU can leverage BugZero to identify their third-party hardware and software bugs, and automatically create tasks in their ITSM tool to address those risks.
BugZero follows a unique, yet intuitive approach to detecting Operational Defects. The image below depicts how BugZero identifies operational defects in vendor systems and notifies you of potential risks.
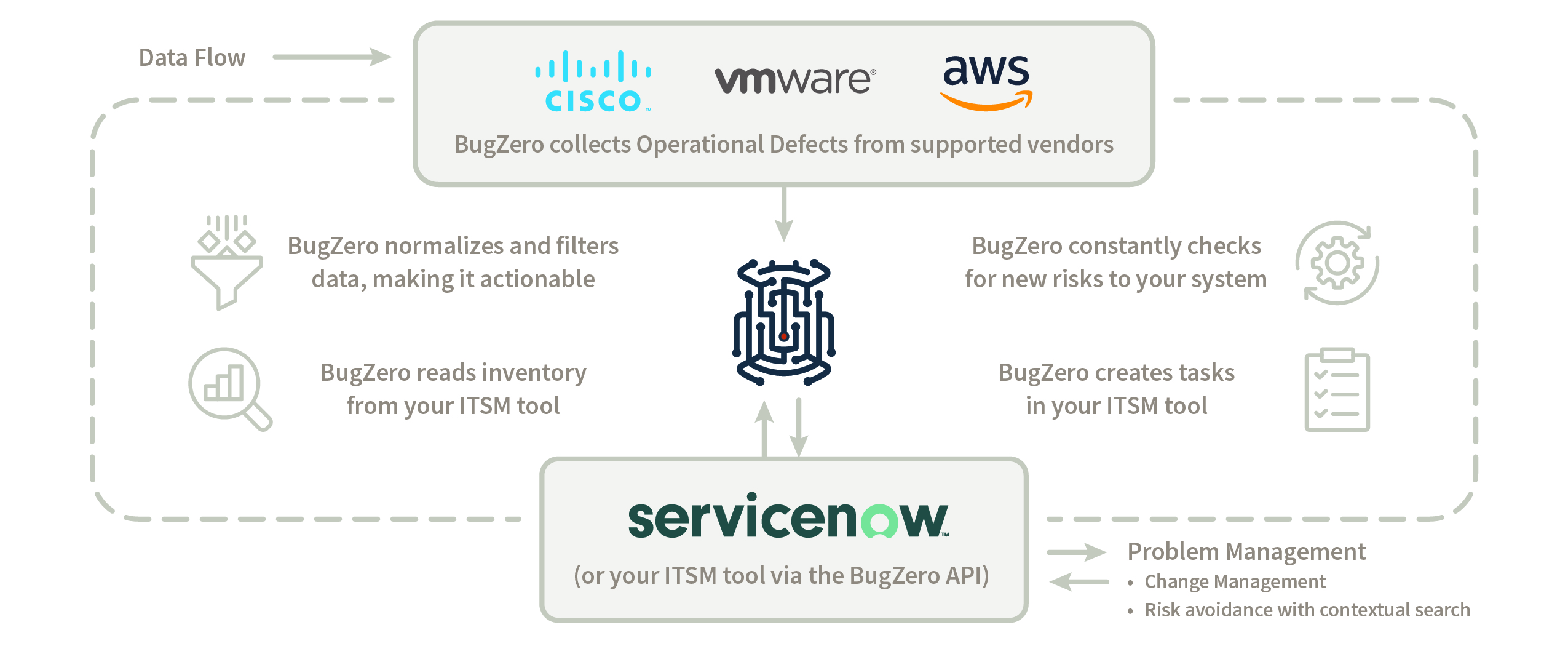
BugZero is currently the only solution in the operational defects space. DORA-compliant firms will benefit from the following features.
BugZero aggregates multi-vendor operational defect data, giving organizations comprehensive information on potential risks. This not only aids in meeting DORA’s mandate for ICT risk management, but empowers IT teams to proactively assess and understand risks throughout their entire IT infrastructure, aligning with DORA’s requirements for resilience testing.
By mapping every vendor operational defect to the affected system, BugZero streamlines reporting of ICT-related incidents, which is a key requirement of DORA.
Given that BugZero integrates third-party operational defect data, organizations can better manage ICT third-party risks. This aligns with DORA's directive to protect against reliance on third-party vendors. BugZero is the only commercially available platform that meets the DORA Regulatory Technical Standard to "identify and evaluate available software and hardware patches and updates using automated tools."
BugZero's focus on IT operational resilience eliminates the need for bug hunting in third-party vendor products. This aligns with DORA's objective of enhancing digital operational resilience among financial institutions. Additionally, it saves organizations time. With DORA set to be mandatory in January 2025, European financial institutions must focus on how they will become operationally resilient. Guarding against operational defects, especially from third-party vendors, is crucial for organizations relying on digital platforms. Enabling DORA-Compliant Firms with the Best Operational Solutions
BugZero is a first-of-its-kind platform designed specifically for operational resilience. It protects against internal threats and equips organizations for future digital challenges.
Need to become DORA compliant? Contact BugZero to learn more about our solution!
"Our vision is to help IT teams be more proactive, increase uptime, and ultimately have a better work/life balance than is possible today."- Eric DeGrass, Founder of BugZero
Discover even more implications of DORA for your firm by diving into our whitepaper: "Building Operational Resilience into your Continuous Compliance Framework."


Eric DeGrass
March 14th, 2024


Gary Harrison
March 13th, 2025


Eric DeGrass
March 13th, 2025
Sign up to receive a monthly email with stories and guidance on getting proactive with vendor risk
BugZero requires your corporate email address to provide you with updates and insights about the BugZero solution, Operational Defect Database (ODD), and other IT Operational Resilience matters. As fellow IT people, we hate spam too. We prioritize the security of your personal information and will only reach out only once a month with pertinent and valuable content.
You may unsubscribe from these communications at anytime. For information on how to unsubscribe, as well as our privacy practices and commitment to protecting your privacy, check out our Privacy Policy.